As a central authentication repository used by Azure, Azure Active Directory allows you to store objects such as users, groups, or service principals as identities. Azure AD also allows you to use those identities to authenticate with different Azure services. Azure AD authentication is supported for Azure SQL Database, Azure SQL Managed Instance, SQL Server on Windows Azure VMs, Azure Synapse Analytics, and now we are bringing it to SQL Server 2022.
Source: Generally available: Azure Active Directory authentication for SQL Server 2022
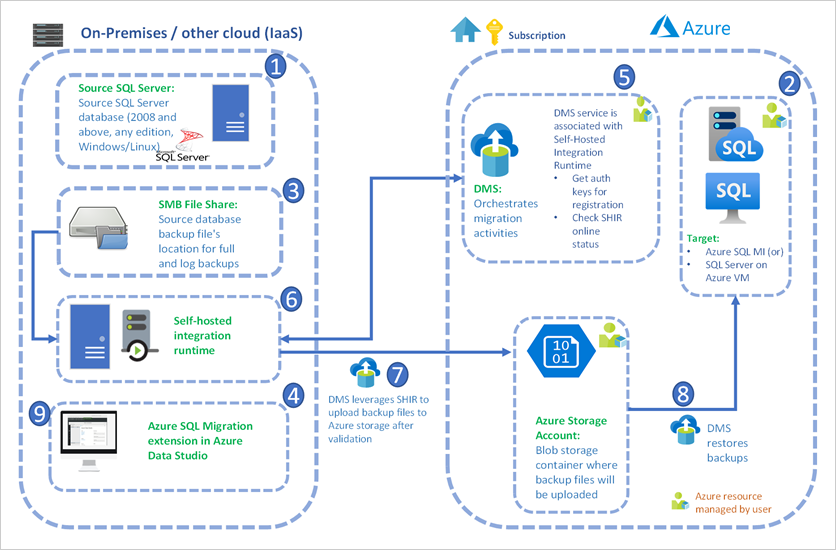
The Azure SQL migration extension for Azure Data Studio enables you to assess, get Azure recommendations and migrate your SQL Server databases to Azure.
Service Tiers
- vCore-based purchasing model
- General Purpose (Scalable compute and storage options)
- Hyperscale (On-demand scalable storage)
- Business Critical (High transaction rate and high resiliency)
- DTU-based purchasing model
- Basic (for less demanding workloads)
- Standard (for workloads with typical performance requirements)
- Premium (for IO-intensive workloads)
Compute Tiers (for General Purpose vCore)
- Provisioned - Compute resources are pre-allocated. Billed per hour based on vCores configured
- Serverless - Compute resources are auto-scaled. Billed per second based on vCore used
Additional Resources
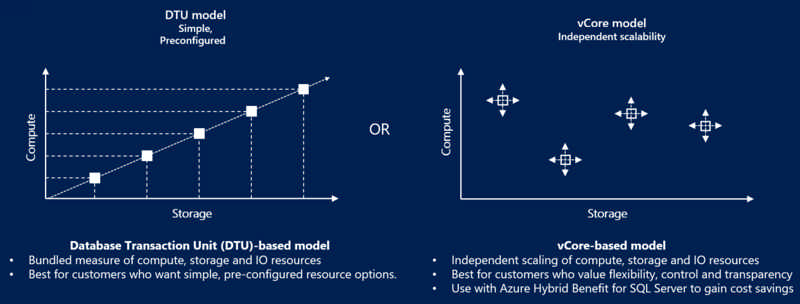
A virtual core (vCore) represents a logical CPU and offers you the option to choose between generations of hardware and the physical characteristics of the hardware (for example, the number of cores, the memory, and the storage size). The vCore-based purchasing model gives you flexibility, control, and transparency of individual resource consumption.
In the vCore-based purchasing model, your costs depend on the choice and usage of Service tier like
- Hardware configuration
- Compute resources (the number of vCores and the amount of memory)
- Reserved database storage
- Actual backup storage
| Use case | General Purpose | Business Critical | Hyperscale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Best for | Most business workloads. Offers budget-oriented, balanced, and scalable compute and storage options. | Offers business applications the highest resilience to failures by using several isolated replicas, and provides the highest I/O performance per database replica. | Most business workloads with highly scalable storage and read-scale requirements. Offers higher resilience to failures by allowing configuration of more than one isolated database replica. |
| Availability | 1 replica, no read-scale replicas, zone-redundant high availability (HA) |
3 replicas, 1 read-scale replica, zone-redundant high availability (HA) |
zone-redundant high availability (HA) (preview) |
| Pricing/billing | vCore, reserved storage, and backup storage are charged. IOPS is not charged. |
vCore, reserved storage, and backup storage are charged. IOPS is not charged. |
vCore for each replica and used storage are charged. IOPS not yet charged. |
| Discount models | Reserved instances Azure Hybrid Benefit (not available on dev/test subscriptions) Enterprise and Pay-As-You-Go Dev/Test subscriptions |
Reserved instances Azure Hybrid Benefit (not available on dev/test subscriptions) Enterprise and Pay-As-You-Go Dev/Test subscriptions |
Azure Hybrid Benefit (not available on dev/test subscriptions) Enterprise and Pay-As-You-Go Dev/Test subscriptions |
For greater details, review resource limits for logical server, single databases, and pooled databases.
The DTU-based purchasing model uses a database transaction unit (DTU) to calculate and bundle compute costs.
A database transaction unit (DTU) represents a blended measure of
- CPU,
- memory,
- reads, and writes
In the DTU-based purchasing model, you can choose between the basic, standard, and premium service tiers for Azure SQL Database.
Choosing a service tier depends primarily on business continuity, storage, and performance requirements.
| Basic | Standard | Premium | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target workload | Development and production | Development and production | Development and production |
| Uptime SLA | 99.99% | 99.99% | 99.99% |
| Maximum backup retention | 7 days | 35 days | 35 days |
| CPU | Low | Low, Medium, High | Medium, High |
| IOPS (approximate)* | 1-4 IOPS per DTU | 1-4 IOPS per DTU | >25 IOPS per DTU |
| IO latency (approximate) | 5 ms (read), 10 ms (write) | 5 ms (read), 10 ms (write) | 2 ms (read/write) |
| Columnstore indexing | N/A | S3 and above | Supported |
| In-memory OLTP | N/A | N/A | Supported |
Review DTU service tiers to learn more.
Azure SQL is a family of managed, secure, and intelligent products that use the SQL Server database engine in the Azure cloud.
- Azure SQL Database: Support modern cloud applications on an intelligent, managed database service, that includes serverless compute.
- Azure SQL Managed Instance: Modernize your existing SQL Server applications at scale with an intelligent fully managed instance as a service, with almost 100% feature parity with the SQL Server database engine. Best for most migrations to the cloud.
- SQL Server on Azure VMs: Lift-and-shift your SQL Server workloads with ease and maintain 100% SQL Server compatibility and operating system-level access.
Azure SQL is built upon the familiar SQL Server engine, so you can migrate applications with ease and continue to use the tools, languages, and resources you're familiar with. Your skills and experience transfer to the cloud, so you can do even more with what you already have.
Azure SQL Database and SQL Managed Instance share a common code base with the latest stable version of SQL Server. Most of the standard SQL language, query processing, and database management features are identical. The features that are common between SQL Server and SQL Database or SQL Managed Instance are:
- Language features - Control of flow language keywords, Cursors, Data types, DML statements, Predicates, Sequence numbers, Stored procedures, and Variables.
- Database features - Automatic tuning (plan forcing), Change tracking, Database collation, Contained databases, Contained users, Data compression, Database configuration settings, Online index operations, Partitioning, and Temporal tables (see getting started guide).
- Security features - Application roles, Dynamic data masking (see getting started guide), Row Level Security, and Threat detection - see getting started guides for SQL Database and SQL Managed Instance.
- Multi-model capabilities - Graph processing, JSON data (see getting started guide), OPENXML, Spatial, OPENJSON, and XML indexes.
Azure manages your databases and guarantees their high-availability. Some features that might affect high-availability or can't be used in PaaS world have limited functionalities in SQL Database and SQL Managed Instance. These features are described in the tables below.
If you need more details about the differences, you can find them in the separate pages:
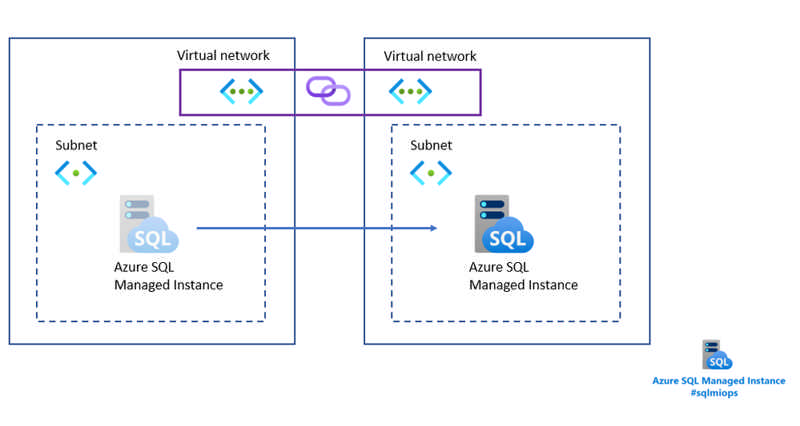
In this blog, we will present a feature for moving Azure SQL Managed Instance from one to another subnet located in a different virtual network. This capability comes as an enhancement of the existing capability for moving the instance to another subnet.
Read more at Azure Daily 2022
Firewall rules in Azure SQL Database control which IP addresses can connect to your database server. Configuring these rules correctly ensures that only trusted users and applications access your data while keeping it secure from unauthorized traffic.
Azure provides two levels of firewall configuration: server-level and database-level rules. Server-level rules allow access to all databases under a logical server, while database-level rules apply only to a specific database.
You can configure firewall rules using the Azure Portal, Transact-SQL (T-SQL) commands, or PowerShell. Understanding how and where to apply these rules helps ensure a secure and flexible environment for managing database access.
Comments