JavaScript
This video tutorial provides a hands-on introduction to jsTree. The walkthrough covers the setup process, basic configuration, and demonstrates how to create a simple tree structure using the library. It’s aimed at developers looking for a quick start with jsTree and practical examples of how it integrates into HTML pages.
Highlights from the video:
- Download and setup of jsTree
- Adding a basic tree structure with static data
- Using plugins like
checkboxandsearch - Tips for integration and customization
While the video is specific to jsTree, the concepts are transferable to similar tree view libraries.
jsTree is a lightweight jQuery plugin that enables the creation of interactive tree views within web applications. It supports themes, drag-and-drop, keyboard navigation, and various data formats including JSON and HTML. Developers can extend it with plugins for checkboxes, search, context menus, and more.
Key features include:
- JSON and HTML data support
- Drag-and-drop functionality
- Highly customizable themes
- Plugin architecture
- Accessibility and keyboard support
jsTree is well-suited for projects that still leverage jQuery and need quick integration of hierarchical navigation or selection UIs.
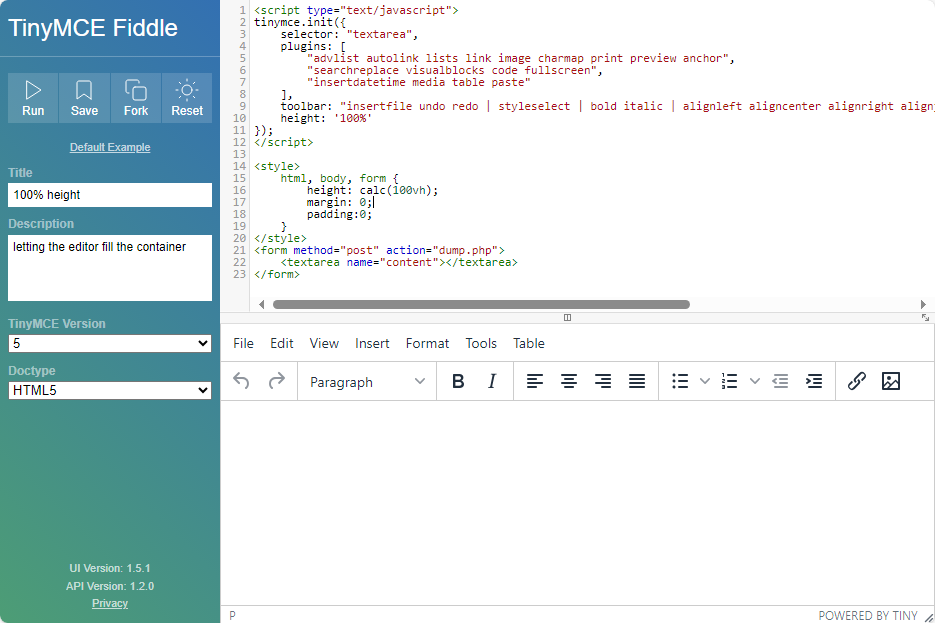
TinyMCE Fiddle is an online platform that allows developers to experiment with and test TinyMCE editor configurations in real-time. It provides a user-friendly interface to modify settings, integrate plugins, and preview changes instantly, facilitating efficient development and customization of the TinyMCE rich-text editor.
Go to TinyMCE Fiddle
JavaScript functions are reusable blocks of code that perform specific tasks. Defined using the function keyword or as arrow functions, they can accept parameters and return values. Functions enhance code organization, modularity, and reusability, allowing developers to execute the same logic multiple times throughout a program with ease.
Make Axios send cookies in its requests automatically.
You can use the withCredentials property.
axios.get(BASE_URL + '/todos', { withCredentials: true });Also it is possible to force credentials to every Axios requests
axios.defaults.withCredentials = trueOr using credentials for some of the Axios requests as the following code
const instance = axios.create({
withCredentials: true,
baseURL: BASE_URL
})
instance.get('/todos')Arrays are ordered collections of values, and they are perhaps the most commonly used data structure in JavaScript. Elements in an array can be accessed by their index, and arrays can hold values of different data types.
let myArray = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
console.log(myArray[0]); // Accessing the first element
Objects in JavaScript are collections of key-value pairs. They are versatile and can be used to represent a wide range of data structures. Objects are often used for creating dictionaries, maps, and records.
let person = {
name: "Maria",
age: 28,
city: "New York"
};
console.log(person.name); // Accessing a propertyKeys are always strings (or Symbols, introduced in ES6). When you use non-string values as keys in an object, JavaScript implicitly converts them to strings.
Objects are generally used for a simple dictionary-like structure with string keys.
Question: How can I check if a string is empty?
Option 1: Check using ""
if (str === "") {
}Note: to know if it's an empty string use === instead of ==. This is because === will only return true if the values on both sides are of the same type, in this case a string. for example: (false == "") will return true, and (false === "") will return false.
Option 2: Check length of string
if (!str || str.trim().length === 0) {
}A callback is a function passed as an argument to another function. This technique allows a function to call another function. A callback function can run after another function has finished.
Example
Using a callback, you could call the calculator function (myCalculator) with a callback (myCallback), and let the calculator function run the callback after the calculation is finished:
function myDisplayer(some) {
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = some;
}
function myCalculator(num1, num2, myCallback) {
let sum = num1 + num2;
myCallback(sum);
}
myCalculator(5, 5, myDisplayer);In the example above, myDisplayer is a called a callback function.
It is passed to myCalculator() as an argument.
Note
When you pass a function as an argument, remember not to use parenthesis.
Right: myCalculator(5, 5, myDisplayer);
Wrong: myCalculator(5, 5, myDisplayer());
The spread (...) syntax allows an iterable, such as an array or string, to be expanded in places where zero or more arguments (for function calls) or elements (for array literals) are expected.
Spread operator doing concat
let arrayOne = [1, 2, 3];
let arraryTwo = [4, 5];
arrayCombined = [...arrayOne,...arrayTwo];Add item using spread operator
let arrayOne = [1, 2, 3];
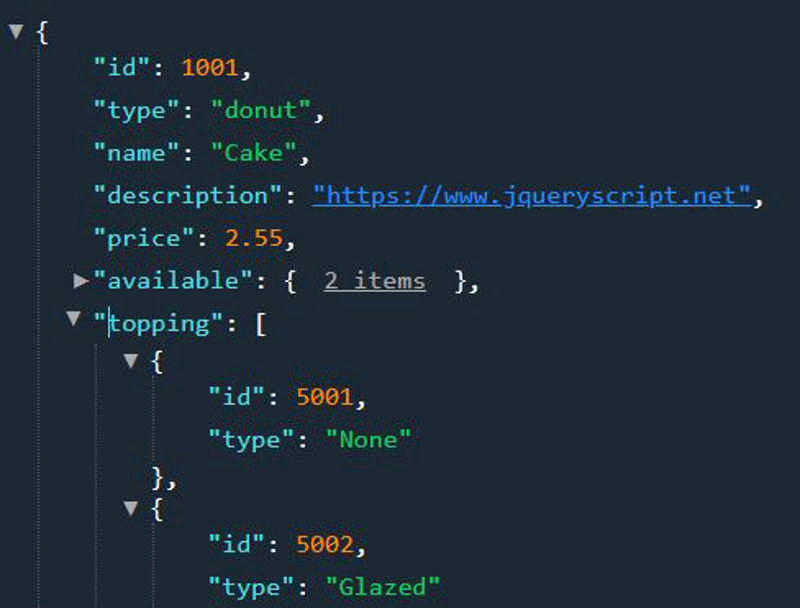
arrayNew = [...arrayOne, 3];A lightweight, simple, beautiful JSON viewer and editor plugin helps the developers to render JSON objects in HTML with collapsible/expandable navigation just like a tree view.
You could configure the toolbar with some basic formatting with an option forecolor to change the text color, options link and image to insert links and images, plus an option code to open the source code view.
<script type="text/javascript">
tinymce.init({
selector: "textarea",
menubar: false,
plugins: "link image code",
toolbar: 'undo redo | styleselect | forecolor | bold italic | alignleft aligncenter alignright alignjustify | outdent indent | link image | code'
});
</script>
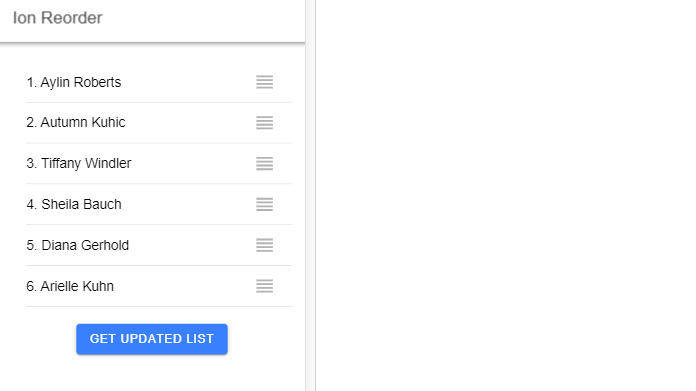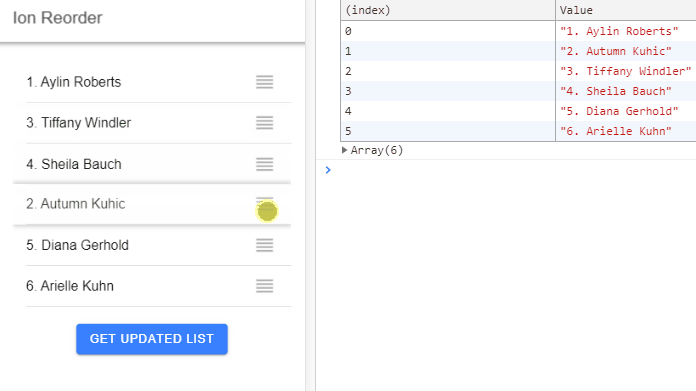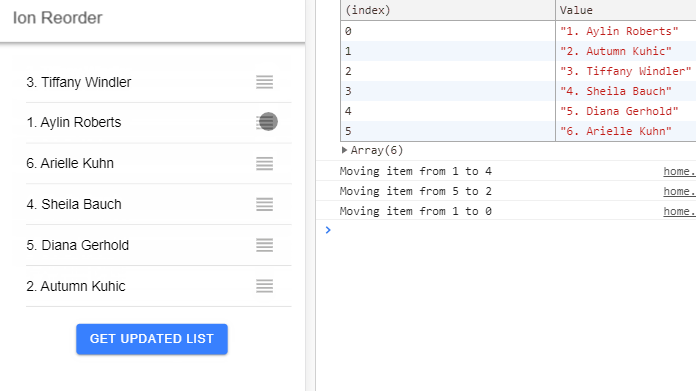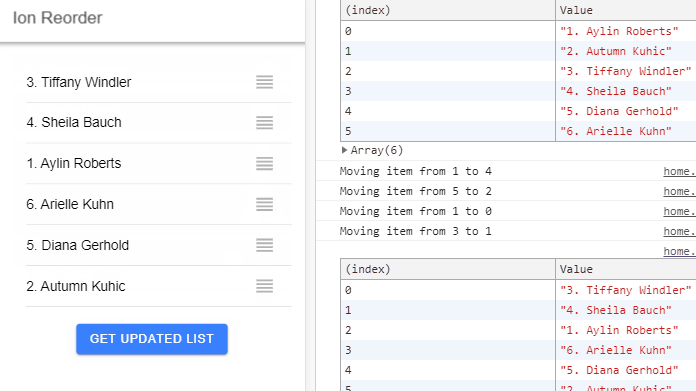
In this Ionic 5/4 tutorial, we’ll discuss how to add a Sortable list with Drag and Drop feature using the Ion Reorder UI component in Ionic Angular application.
Bootstrap Dropdown Filter is a small and simple jQuery plugin that adds an input-based live filter capability to your Bootstrap dropdown list.
Easy jQuery Input Filter For Bootstrap Dropdown List | Free jQuery Plugins (jqueryscript.net)
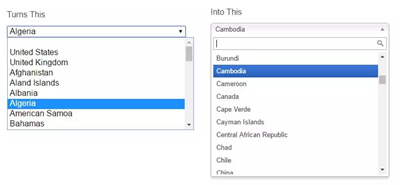
Chosen is an extensive plugin that not only restyles your select elements but provides additional functionality such as in-select searching, multiple element selection, and highlighting.
zTree
Fancy Tree
jQuery and jQuery UI Dynamic Tree View Plugin - Fancytree | Free jQuery Plugins (jqueryscript.net)
Other Tree View Resources
Expando is a tiny jQuery-powered JS Object Viewer/Editor that helps developers creates a very nice expandable tree hierarchy of your data.
With this plugin you can create an editable tree with collapsible branches to easily browse/edit JavaScript objects and their properties.
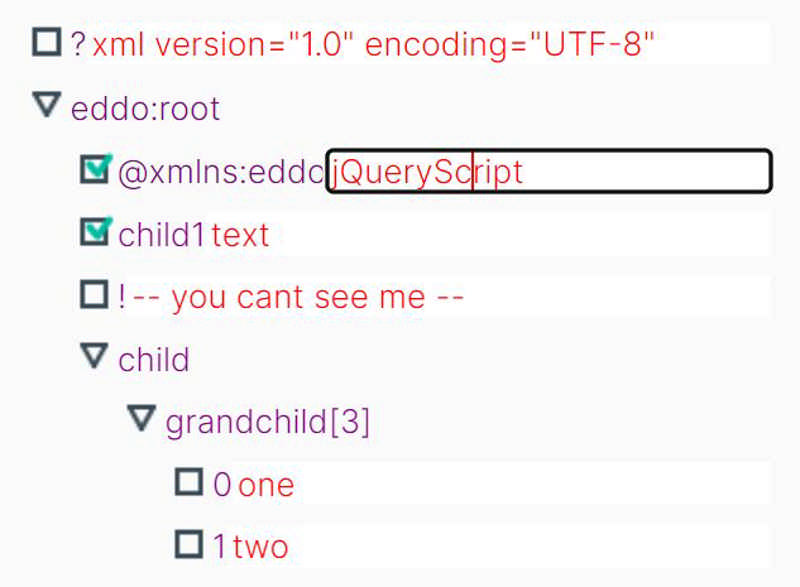
Tree-style Expanding JS Object Viewer/Editor In jQuery - Expando
The Vanilla JavaScript version of the jQuery JSON Path Picker, which helps you render your JSON data in a collapsible tree structure where you can get the path to each key by clicking on the output icon.

A super lightweight, pure JavaScript JSON formatter / viewer which helps render JSON objects just like a collapsible tree view.

Yet another JSON viewer library that renders your JSON data as a collapsible and expandable tree structure for better readability.
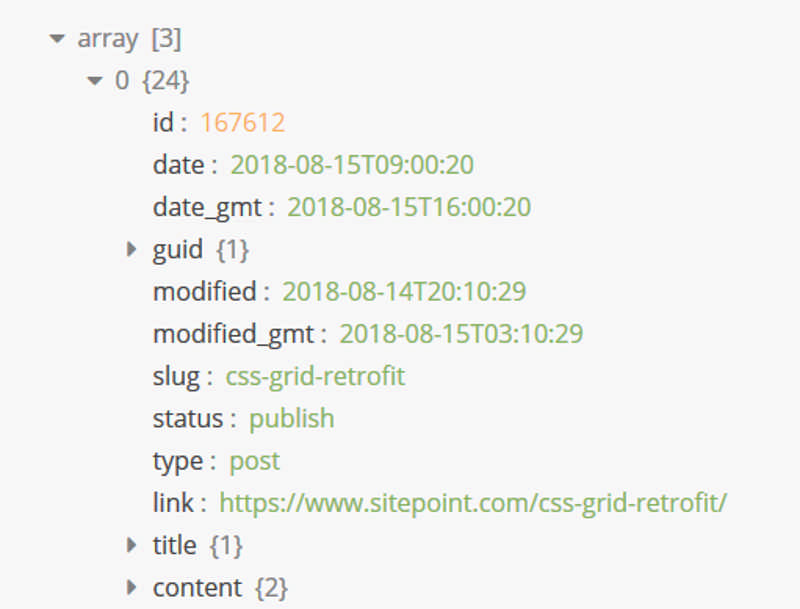
Yet another jQuery JSON viewer plugin that renders JSON objects in HTML with support for syntax highlighting and collapsible/expandable navigation.

- .NET
- Agile
- AI
- ASP.NET Core
- Azure
- C#
- Cloud Computing
- CSS
- EF Core
- HTML
- JavaScript
- Microsoft Entra
- PowerShell
- Quotes
- React
- Security
- Software Development
- SQL
- Technology
- Testing
- Visual Studio
- Windows